Theoretical Foundations of MA Processes
Time Series Nature & Invertibility
Definition:
MA(\(q\)) model:
\(Y_t = \epsilon_t + \theta_1 \epsilon_{t-1} + \cdots + \theta_q \epsilon_{t-q}\)
where \(\epsilon_t \sim WN(0,\sigma^2)\)
Key Properties:
- Models shock persistence through lagged errors
- ACF cuts off after lag \(q\) (distinct signature)
- PACF tails off gradually
- Requires invertibility (roots of \(1 + \theta_1 z + \cdots + \theta_q z^q = 0\) lie outside unit circle)
Simulating & Diagnosing MA Processes
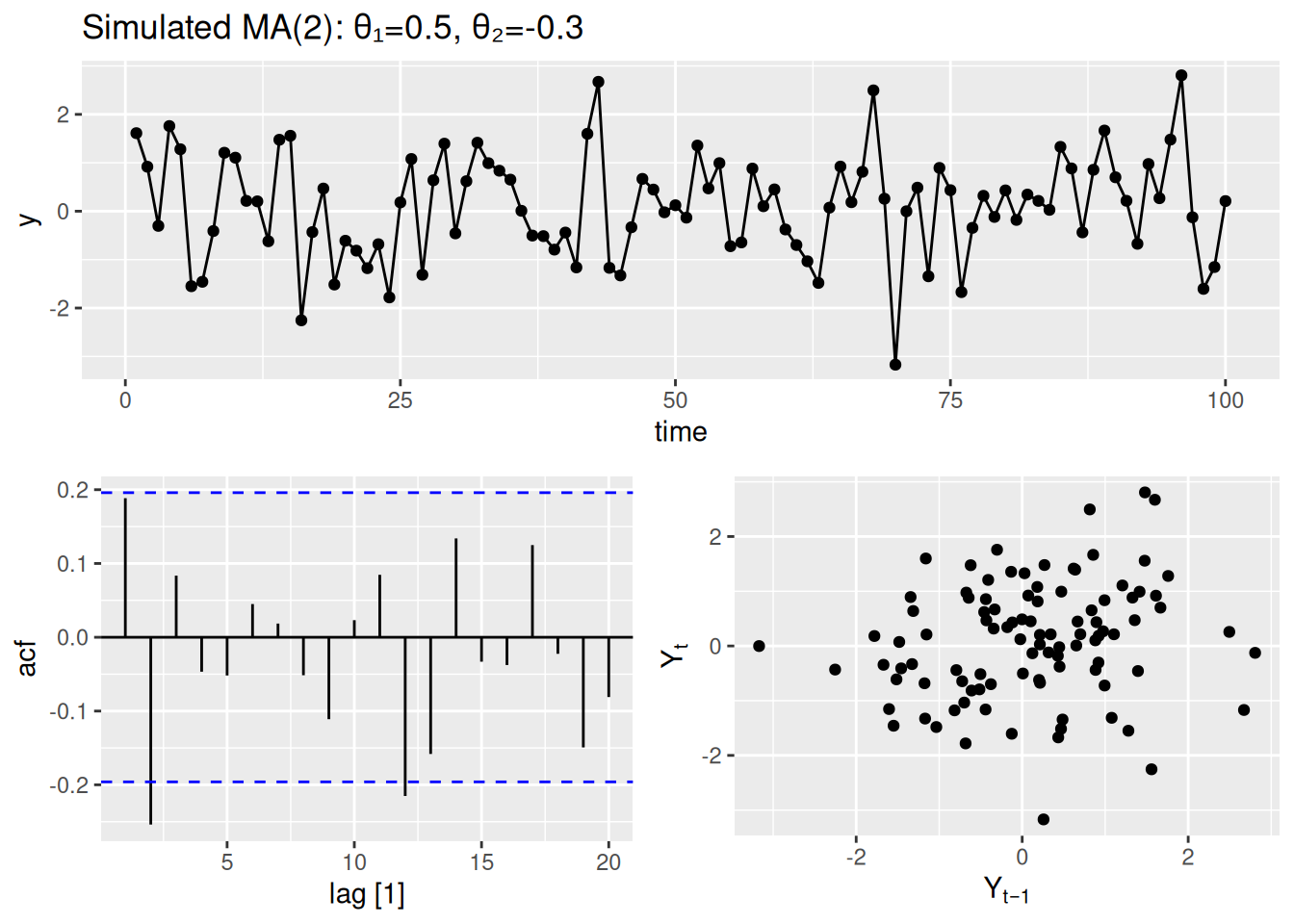
Simulated MA(2) Process
library(fable)
set.seed(123)
ma_data <- tibble(
time = 1:100,
y = arima.sim(model = list(ma = c(0.5, -0.3)), n = 100) # θ₁=0.5, θ₂=-0.3
) %>% as_tsibble(index = time)
ma_data %>%
gg_tsdisplay(y, plot_type = "scatter") + # Observe ACF cutoff at lag 2
labs(title = "Simulated MA(2): θ₁=0.5, θ₂=-0.3")
Model Estimation & Diagnostics
fit_ma <- ma_data %>%
model(ARIMA(y ~ pdq(0,0,2))) # Explicit MA(2) specification
report(fit_ma) # Check θ estimates vs true values (0.5, -0.3)
Series: y
Model: ARIMA(0,0,2)
Coefficients:
ma1 ma2
0.5477 -0.3881
s.e. 0.0911 0.0908
sigma^2 estimated as 0.8128: log likelihood=-131.49
AIC=268.98 AICc=269.23 BIC=276.8
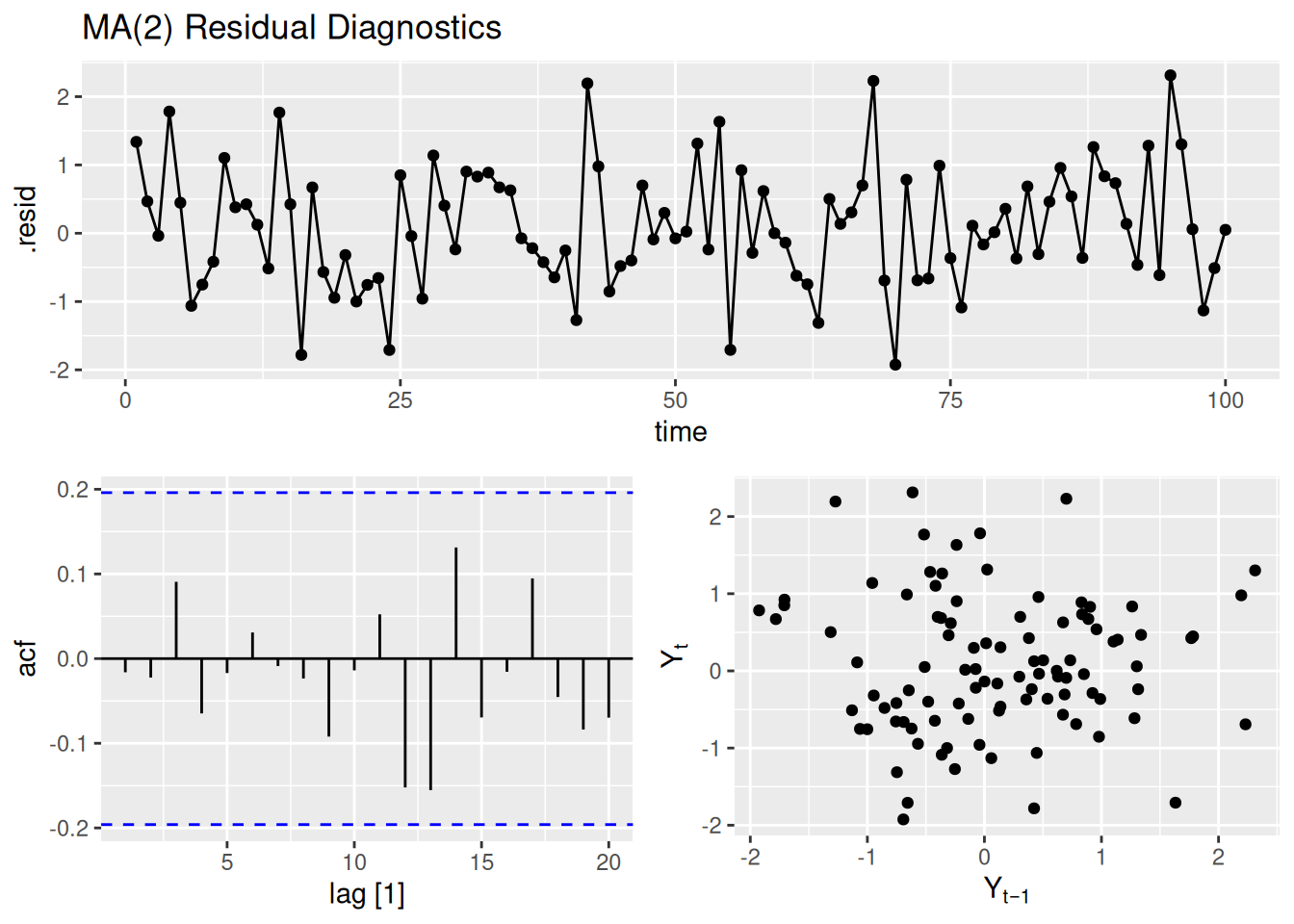
fit_ma %>%
residuals() %>%
gg_tsdisplay(plot_type = "scatter") +
labs(title = "MA(2) Residual Diagnostics")
Real-World Case Study: US Consumption
Lab Activity A: Modeling Consumption with MA
1. Data Preparation
2. Exploratory Analysis
3. MA Order Identification
4. Model Fitting
5. Residual Diagnostics
6. Forecasting
Lab Activity B: Modeling US Production
1. Data Preparation
2. Visualize Series
3. MA Order Selection
Determine appropriate MA order through ACF:
4. Model Comparison
Fit competing specifications and evaluate:
5. Policy-Relevant Forecasting
Using the best model, generate forecasts up-to 10 time points into the future and interpret economic meaning:
Key Concepts Cheat Sheet
| ACF |
Cuts off at lag \(q\) |
Tails off gradually |
| PACF |
Tails off gradually |
Cuts off at lag \(p\) |
| Condition |
Invertibility (roots > 1) |
Stationarity (roots < 1) |
| Use Case |
Short-lived shock effects |
Long-term dependencies |